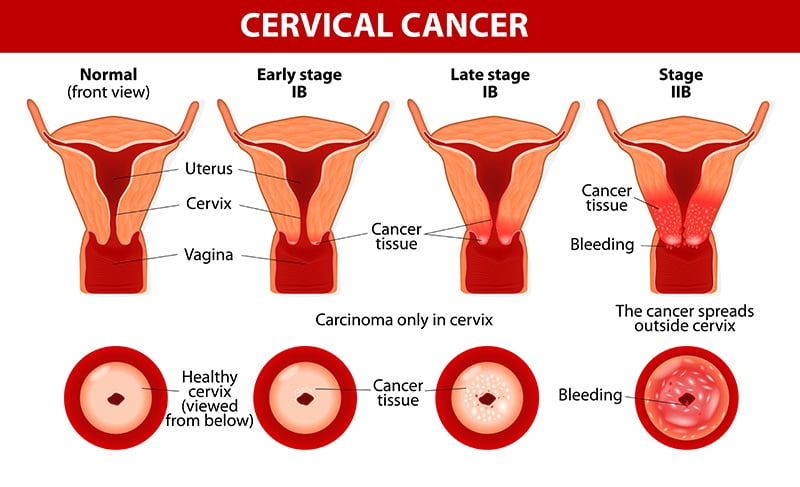
Cervical cancer is a type of cancer that occurs in the cells of the cervix, the lower part of the uterus that connects to the vagina. While it was once one of the leading causes of cancer death for women in India, advancements in screening and prevention can significantly reduce its incidence and mortality rates. However, it remains a significant global health concern, particularly in low-income and middle-income countries where access to preventive measures and healthcare services may be limited.
Union Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman in her interim budget speech on 1st March 2024 , said that the government will encourage vaccination for girls in the age group of 9 to 14 years for the prevention of cervical cancer.
“Our government will encourage vaccination for girls in the age group of 9-14 years to prevent cervical cancer,” Ms Sitharaman said while presenting the interim budget 2024 in the Lok Sabha.
Ms Sitharaman emphasized the government’s plans to set up more medical colleges and said that the government aims to serve the people through improved healthcare services.
Symptoms of Cervical cancer
Early-stage cervical cancer may not cause any symptoms, which is why regular screenings are crucial for early detection. However, as the cancer progresses, women may experience the following symptoms:
- Abnormal vaginal bleeding, such as bleeding between periods, after intercourse, or after menopause.
- Pelvic pain or pain during sexual intercourse.
- Unusual vaginal discharge that may be watery, bloody, or foul-smelling.
Risk Factors
Several factors may increase a woman’s risk of developing cervical cancer, including:
- Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection: HPV is a common sexually transmitted infection that plays a significant role in the development of cervical cancer.
- Smoking: Women who smoke are at a higher risk of developing cervical cancer compared to non-smokers.
- Weak immune system: Conditions or medications that weaken the immune system increase the risk of cervical cancer.
- Early sexual activity: Having sexual intercourse at an early age increases the likelihood of HPV infection.
- Multiple sexual partners: Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of HPV infection, which can lead to cervical cancer.
- Lack of regular Pap tests: Regular Pap tests (Pap smears) can detect precancerous changes in the cervix early, allowing for timely intervention.

Prevention from Cervical cancer
Preventive measures can significantly reduce the risk of developing cervical cancer:
- HPV vaccination: Vaccination against HPV is recommended for both boys and girls aged 11-12, although it can be administered as early as age 9. The vaccine is most effective when given before sexual activity begins.
- Regular screenings: Pap tests and HPV tests are essential for detecting abnormal changes in the cervix early. Women should follow their healthcare provider’s recommendations for screening frequency.
- Safe sexual practices: Practicing safe sex, including using condoms, can reduce the risk of HPV infection.
- Avoiding smoking: Quitting smoking can lower the risk of cervical cancer and other health problems.
- Building a strong immune system: Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and managing stress, can help support a strong immune system.

Conclusion
Cervical cancer is a highly preventable and treatable disease when detected early through regular screenings and preventive measures. It’s essential for women to prioritize their reproductive health by scheduling regular check-ups with their healthcare providers and discussing any concerns or symptoms they may have. Early detection and intervention can significantly improve outcomes and save lives.